Difference between revisions of "Bandit - Static Code Analyss for Python Code"
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
This example is using the Bandit example files from their github (https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit). For this case we are using the imports.py Example with the following Source Code: | This example is using the Bandit example files from their github (https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit). For this case we are using the imports.py Example with the following Source Code: | ||
import | import os | ||
import pickle | |||
import sys | |||
import subprocess | |||
After executing bandit on the File | After executing bandit on the File | ||
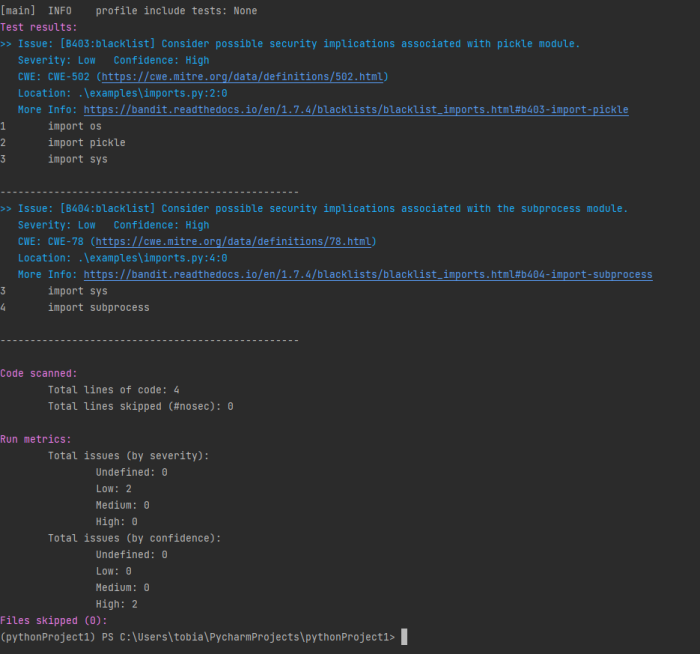
bandit imports.py | bandit imports.py | ||
you get the following output | you get the following output: | ||
[[File:2023-01-14 21 07 27-Window.png|700px|al]] | [[File:2023-01-14 21 07 27-Window.png|700px|al]] | ||
Bandit has found two Low Severity Issues regarding Problems with the imported Packages. A detailed information is given for every Issue found. It also shows the CWE Number associated with it. | Bandit has found two Low Severity Issues regarding Problems with the imported Packages. A detailed information is given for every Issue found. It also shows the CWE Number associated with it. | ||
== Results == | |||
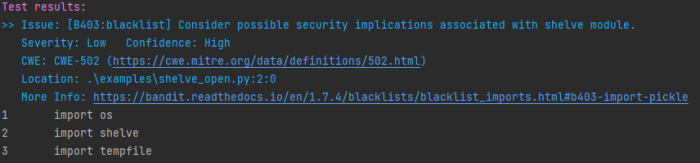
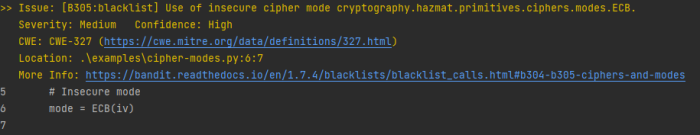
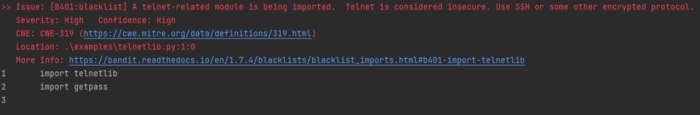
Bandit categorizes possible Problems into three Risk Categories Low, Medium, High each combined with a Confidence Score of Low, Medium High. This shows the impact of the Issue and how confident Bandit is, that this is really an issue. | |||
[[File:Low Risk.png|700px|al]] | |||
[[File:Medium_Risk.png|700px|al]] | |||
[[File:High_Risk.png|700px|al]] | |||
== References == | == References == | ||
| Line 67: | Line 48: | ||
* https://pypi.org/project/bandit/#files | * https://pypi.org/project/bandit/#files | ||
* https://bandit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/start.html | * https://bandit.readthedocs.io/en/latest/start.html | ||
[[Category:Documentation]] | [[Category:Documentation]] | ||
Latest revision as of 09:05, 31 January 2023
Summary
This documentation shows how to install and use Bandit, a static analysis tool for C/C++ source code. This Tool can be used to identify possible Security risks categorized in three different Severity Levels (Low, Medium, High).
Requirements
- Python Version 3.7 or higher
- Python Package: bandit
Installation and Usage
Bandit can be easily installed via the pip install command. Furthermore it can be found on PyPi for manual installation. If you want to install it manually please follow the attached References.
pip install bandit
For executing the analysis just enter die File or Folder you want to be analyzed in a Python Terminal
bandit <File/Folder>
Example
This example is using the Bandit example files from their github (https://github.com/PyCQA/bandit). For this case we are using the imports.py Example with the following Source Code:
import os import pickle import sys import subprocess
After executing bandit on the File
bandit imports.py
you get the following output:
Bandit has found two Low Severity Issues regarding Problems with the imported Packages. A detailed information is given for every Issue found. It also shows the CWE Number associated with it.
Results
Bandit categorizes possible Problems into three Risk Categories Low, Medium, High each combined with a Confidence Score of Low, Medium High. This shows the impact of the Issue and how confident Bandit is, that this is really an issue.