Difference between revisions of "Flipper Zero"
(→NFC: typo fixed) |
(Infrared added) |
||
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
=== Infrared === | === Infrared === | ||
Withe the Infrared sender and receiver it is possible to send well-known Infrared signals or learn new more unique signals to later on emulate them. | |||
Examples for well-known remote signals that are already integrated into the Flipper Zero include: | |||
- TVs | |||
- HVACs | |||
- Beamers | |||
- Ventilators | |||
If the goal is to turn on a TV the Flipper Zero bruteforces the correct signal by looping through every known TV "on" signal it has stored. | |||
If a device remote signal is not yet known to the Flipper Zero it can be easily added by pressing the original remote once towards the Flipper Zero while the "learning mode" is active. This can be achieved by starting the tool "Learn New Remote" inside the Infrared category. | |||
=== GPIO === | === GPIO === | ||
=== iButton === | === iButton === | ||
Revision as of 08:11, 27 February 2023
Summary
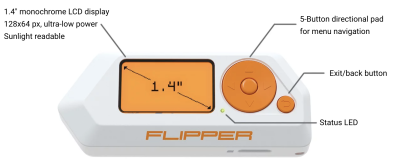
The Flipper Zero is a gadget for penetration testers, system administrators and tech enthusiasts created by Flipper Devices Inc. The device allows capturing and transmitting of various Sub-GHz signals, such as Garage Openers or NFC chips, as-well as Infrared signals. Furthermore the device can be used as a Bad USB Stick and offers iButton capabilities. Thanks to its small form factor it is a perfect device for covert operations.
Description
Setting up the Flipper Zero
- Open the box containing the Flipper Zero and boot it by holding down the back button
- To use the full potential of the Flipper Zero an Micro SD-Card is needed. Insert it into the right bottom of the flipper with the pins of the SD-Card facing upwards.
- After successful installation of the Micro SD-Card, a little SD-Card symbol appears on the top left of the Flipper Zero GUI.
- Finally for the best experience the Firmware should be updated, this point is explained in more detail in the section "Firmware Update".
Firmware Update
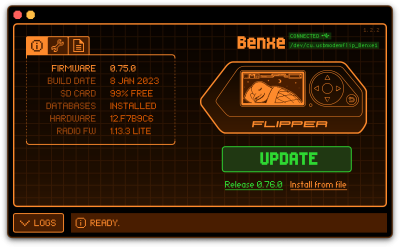
To update the device either connect the Flipper Zero to a PC via a USB-C cable or connect it to a mobile phone using Bluetooth and use the "Flipper" app. In this guide a PC is used for the firmware update.
- First download qFlipper from the official Flipper Zero website https://flipperzero.one/update
- After installation start the application and connect the Flipper Zero, it should show the connected device in the GUI.
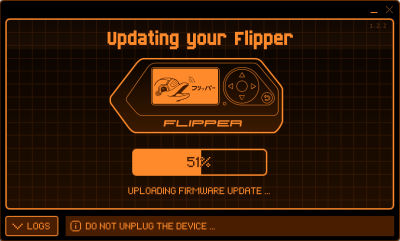
- Next click the Update button to initiate the update process, this process can take a few minutes.
- After successfully updating the device, the qFlipper software shows the new version number and the Flipper Zero displays "Firmware update success". Now the device is ready to be used again.
Use Cases
As already mentioned there are many different use cases for the Flipper Zero, such as Sub-GHz signal analyzing and cloning, NFC spoofing or controlling of Infrared devices. In this section some examples for different use cases will be given as well as a basic explanation of how various attacks can be performed.
The use cases are divided into the corresponding categories of the Flipper Zero.
Sub-GHz
With the Sub-GHz module various attacks up to 50 meters are possible in the following bands, 300-348 MHz, 387-464 MHz, and 779-928 MHz.
A basic attack in this regard would be the cloning of a garage door remote signal, to freely open and close a garage door. For this to work the Flipper Zero first needs to be configured to the corresponding band of the original garage remote.
- First open the "Frequency Analyzer" tool inside the Sub-GHz category.
- Press the garage door remote to send out a signal.
- The Flipper Zero will automatically display the frequency of the captured signal.
- Next go back and open the "Read" tool
- Open the config with the *left* button and set the appropriate frequency band from the captured signal
- Press the garage door remote again and if the Flipper Zero supports the protocol it will be possible to save the opening signal
- If the Flipper Zero does not detect a valid signal, try to modify the modulation in the settings of the "Read" tool or it could be possible that the Flipper Zero does not yet support the protocol of the garage door.
After a signal is captured it is possible to either save or discard it. Saved signals can be triggered via the "Saved" menu. Using this it is possible to create clones of existing garage door remotes. This is just a basic attack, but it shows the capabilities of the Flipper Zero very clearly, not only garage door remotes can be cloned and utilized, almost anything inside the supported range spectrum can be easily copied and used accordingly. Only difference in this regards would be if the devices use a so called "rolling code". If rolling codes are used a signal can be read and cloned but is useless, as the underlying "code" is unknown. The most probable outcome copying such as signal and resending it would be that the original sender gets blocked by the garage door or the corresponding receiver.
125 kHz RFID
NFC
With the NFC module the reading, saving and writing of 13.56 MHz NFC signals is possible. This ranges from key cards, like hotel entry cards and door openers, to toys that utilize NFC signals.
- First open the "Read" tool inside the NFC category.
- Next hold the Flipper Zero close next to the desired key card.
- As soon as the Flipper Zero detects the card it will start decrypting the sectors of it.
- If well-known keys are used and the key card can be decrypted it is possible to save the key card for later emulation or writing onto a blank NFC card.
With this various hotel key cards can be easily copied and used. The success of such an attack is based on the used keys to encrypt the sectors of the NFC Cards in use. If the Flipper Zero knows the keys, e.g. the NFC key card utilizes well-known keys for encryption, a successful decryption and cloning of the NFC key card is almost guaranteed. If the key card uses a special token for authentication by generating a unique code every time the card is read, it is not possible to clone the card (or atleast not with the Flipper Zero). An example for this would be the NFC key card for a Tesla vehicle.
Infrared
Withe the Infrared sender and receiver it is possible to send well-known Infrared signals or learn new more unique signals to later on emulate them. Examples for well-known remote signals that are already integrated into the Flipper Zero include:
- TVs - HVACs - Beamers - Ventilators
If the goal is to turn on a TV the Flipper Zero bruteforces the correct signal by looping through every known TV "on" signal it has stored. If a device remote signal is not yet known to the Flipper Zero it can be easily added by pressing the original remote once towards the Flipper Zero while the "learning mode" is active. This can be achieved by starting the tool "Learn New Remote" inside the Infrared category.