Difference between revisions of "Machine in the Middle (MitM) - General"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Think of a MitM attack like this: | Think of a MitM attack like this: | ||
[[File:BasicMitM.png]] | [[File:BasicMitM.png|500px]] | ||
In the picture, the MitM was between a client (user) and a web server providing a website. | In the picture, the MitM was between a client (user) and a web server providing a website. | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Think of spoofing like this: | Think of spoofing like this: | ||
[[File:BasicSpoofing.png]] | [[File:BasicSpoofing.png|500px]] | ||
== How are Machine-in-the-Middle attack (Tools) working? == | == How are Machine-in-the-Middle attack (Tools) working? == | ||
Revision as of 12:36, 2 January 2024
Summary
This documentation aims to provide a general description of Machine-in-the-Middle (MitM) attacks and two examples of tools - Ettercap and Bettercap - are given. Note that MitM is a very broad term and a lot of aspects, methodologies, and tools will fall into this category. Especially in practice, people will often use the term "MitM" in a variety of contexts. Therefore, this article should give you just an overview: depending on your specific needs and goals a deeper dig into related documentation of the technologies and tools will be necessary. You might also firstly search here in the Elvis Wiki whether an article is already provided and you can start working with that.
What is a Machine-in-the-Middle (MitM) attack?
Formerly called “Man-in-the-Middle” attack this is nowadays deprecated as it is not gender-inclusive. Therefore, and to keep the commonly used abbreviation “MitM”, it is nowadays often called Machine-in-the-Middle or sometimes also “Person-in-the-Middle” (PitM).
NIST, the National Institute of Standards and Technology, a very well-known and in the information security industry high renown organization, has the following – compact, though meaningful – definition of what a MitM is: “An attack where the adversary positions themselves between the user and the system so that they can intercept and alter data traveling between them.” (https://csrc.nist.gov/glossary/term/mitm, accessed: 22.12.2023) Please note, that the quotation has been adapted to comply with a gender-neutral language (themselves instead of himself and they instead of he). The definition given above talks about “user” and “system”. In practice, the “user” is often a client (where the human user is working on an Internet-connected device), and the “system” is usually a server that provides services, processes requests, and delivers responses.
In cyber security, it is often the goal of the adversary (or another interested party like security researchers) to gain a MitM position, as it allows this entity to read data (depending on the scenario the data might be e.g., encrypted), modify data, drop data, do further unintended actions or a combination of them.
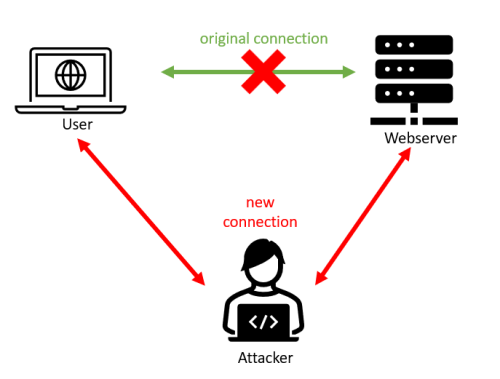
Think of a MitM attack like this:
In the picture, the MitM was between a client (user) and a web server providing a website.
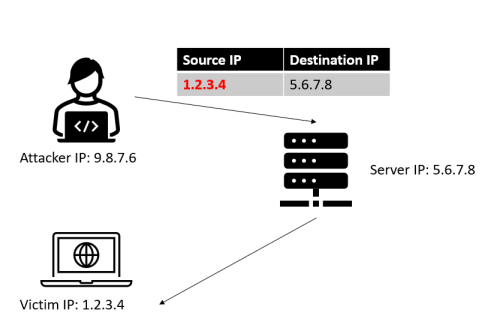
MitM is heavily connected to the concept of ‘spoofing’ where spoofing means, very basically speaking, the faking of the (source) parameter in a protocol to mimic another identity.
Think of spoofing like this:
How are Machine-in-the-Middle attack (Tools) working?
- Operating system: Ubuntu 18.04 bionic amd64
- Packages: git emacs
In order to complete these steps, you must have followed Some Other Documentation before.
How to prevent MitM?
Tools
Ettercap
Enter these commands in the shell
echo foo echo bar
Bettercap
Make sure to read
- War and Peace
- Lord of the Rings
- The Baroque Cycle
Used Hardware
Device to be used with this documentation Maybe another device to be used with this documentation
Courses
- A course where this documentation was used (2017, 2018)
- Another one (2018)