Difference between revisions of "Pocket Science Lab Kit"
(add dummy text; image positioning) |
(finalize structure, add images, add exploits, add attack) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
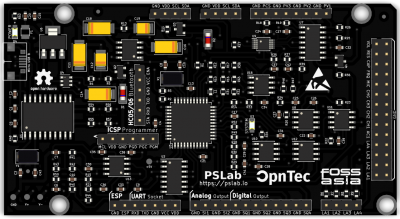
[[File:PSLab v5 top.png|thumb|right|400px||Pocket Science Lab Kit Top View]] | [[File:PSLab v5 top.png|thumb|right|400px||Pocket Science Lab Kit: ''Top View'']] | ||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
The Pocket Science Lab Kit is a small USB-based hardware extension for an Android device or PC, which allows the use of different instruments / functions that are already integrated in the board or can be expanded via external sensors. It is aimed at everyone whether teacher, pupil, hobbyist, student, professor or scientist. The name Pocket Science Lab says it all. The user has a small scientific laboratory in the size of a pocket. The aim of the Pocket Science Lab project is to perceive one's environment better and to digitize the analog world. | The [https://pslab.io/ Pocket Science Lab Kit] is a small USB-based hardware extension for an [https://play.google.com/store/apps/details?id=io.pslab Android device] or [https://github.com/fossasia/pslab-desktop PC], which allows the use of different instruments / functions that are already integrated in the board or can be expanded via external [https://pslab.io/sensors/ sensors]. It is aimed at everyone whether teacher, pupil, hobbyist, student, professor or scientist. The name Pocket Science Lab says it all. The user has a small scientific laboratory in the size of a pocket. The aim of the Pocket Science Lab project is to perceive one's environment better and to digitize the analog world. | ||
== Description == | == Description == | ||
This board allows you measure all kinds of things, assumed you have the right sensor and it is supported. Basic connectors/sensors are USB, GPIO Connector, UART,Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, I2C and ICSP Programmer. A full list of | This board allows you to measure all kinds of things, assumed you have the right sensor, and it is supported. Basic connectors/sensors are ''USB, GPIO Connector, UART, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, I2C'' and ''ICSP Programmer''. A full list of technical specifications can be found on the [https://pslab.io/wp-content/uploads/PSLab-Data-Sheet.pdf datasheet] as well as on the [https://pslab.io/ PS Lab website]. A built-in ''Oscilloscope, Power Source, Multimeter, Accelerometer, Sensors, Logic Analyzer'' and ''Wave Generator'' can be used right out of the box. A ''Temperature Sensor, Compass, Barometer'' and ''Lux Meter'' are not included and need to be bought separately. | ||
=== Functionalities === | === Functionalities === | ||
To control the PS Lab Kit an Android App and PC application are available. From the user-friendly interface a list of various functions can be selected. The functions are listed in the section described above. Each function can record the received input. Therefore, a Rec-Button will appear in the top right corner. The recording can be started by clicking on it and stopped by clicking it another time on it. The menu has a section called: ”Logged Data”. In this section the recording can be found and exported as ''.CSV'' file. | |||
selected. The | |||
input. Therefore a Rec-Button will appear | |||
be started by clicking on it and stopped by clicking another time on it. The menu has | |||
a section | |||
as . | |||
<gallery mode=packed heights=400px> | |||
File:View instrument panel.png|200px|thumb|none|'''Instrument View''' | |||
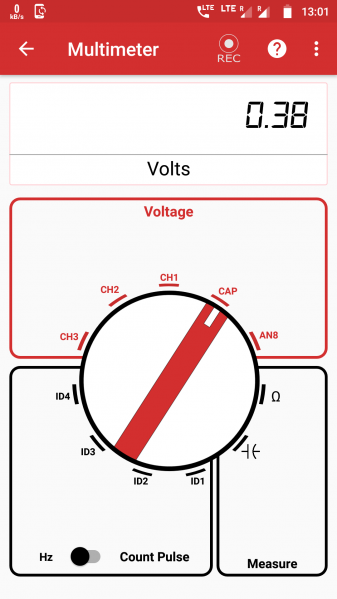
File:Instrument multi meter view.png|200px|thumb|none|'''Multimeter''' | |||
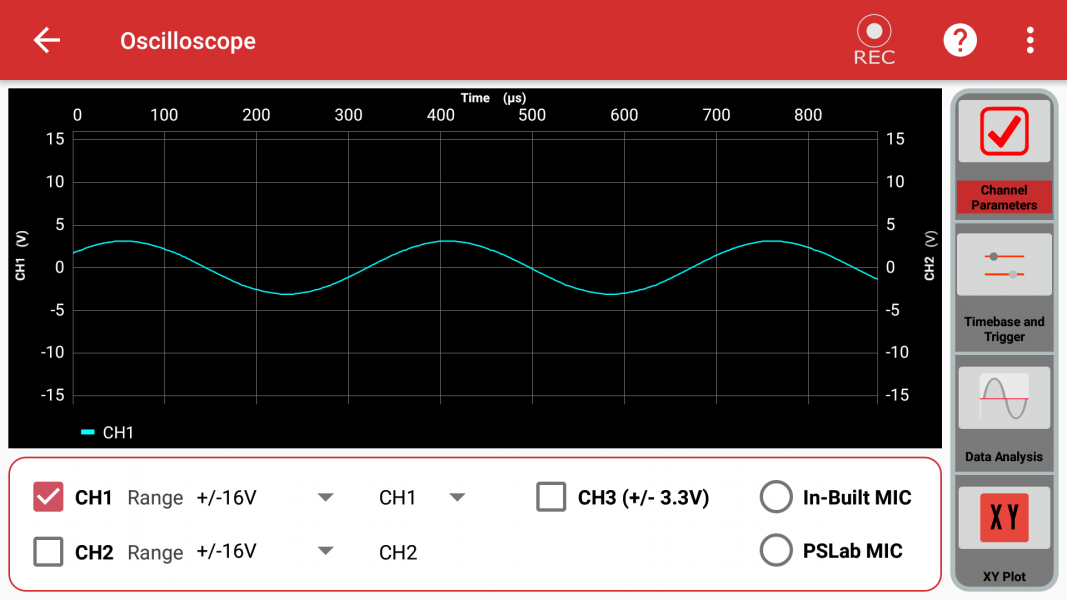
File:Instrument oscilloscope channel view.png|200px|thumb|none|'''Oscilloscope''' | |||
</gallery> | |||
=== Sensors === | === Sensors === | ||
Notable sensors are the temperature sensor, gas sensor and | Notable sensors are the ''temperature sensor, gas sensor'' and ''moisture sensor''. | ||
moisture sensor. | |||
PS Lab Kit | Currently the functionalities of these sensors is unavailable for the PS Lab Kit. The Pocket Science Lab Project provides a list of compatible [https://pslab.io/sensors/ sensors]. | ||
of | |||
<gallery mode=packed heights=250px> | |||
File:LM35.jpg|200px|thumb|none|'''LM35''': ''Temperature Sensor'' | |||
File:MQ135.jpg|200px|thumb|none|'''MQ135''': ''Gas Sensor'' | |||
File:FR-04.jpg|200px|thumb|none|'''FR-04''': ''Rain Sensor'' | |||
</gallery> | |||
=== Wi-Fi === | === Wi-Fi === | ||
[[File:ESP-WROOM-02U.png|thumb|left|163px||ESP8266 DevKitC V1]] | |||
ESP8266-DevKitC is a small-sized ESP8266-based development board produced by Espressif. All the I/O pins of the module are broken out into the female pin headers on both sides of the board for easy interfacing. Developers can connect these pins to peripherals as needed. | |||
The | The Pocket Science Lab Kit can be extended with such a Wi-Fi module. Normally an ESP8266 chip would be soldered to the back of the kit to create network connectivity between the board and the Android phone or PC. The documentation for this is currently not available. | ||
the | |||
== Use Cases == | == Use Cases == | ||
| Line 59: | Line 49: | ||
Oscilliscope text. | Oscilliscope text. | ||
== Exploits == | |||
=== CVE-2019-12586 === | |||
The EAP peer implementation in Espressif ESP-IDF 2.0.0 through 4.0.0 and ESP8266- | |||
NONOS-SDK 2.2.0 through 3.1.0 processes EAP Success messages before any EAP | |||
method completion or failure, which allows attackers in radio range to cause a denial | |||
of service (crash) via a crafted message. | |||
=== CVE-2019-12588 === | |||
The client 802.11 mac implementation in Espressif ESP8266-NONOS-SDK 2.2.0 through | |||
3.1.0 does not validate correctly the RSN AuthKey suite list count in beacon frames, | |||
probe responses, and association responses, which allows attackers in radio range to | |||
cause a denial of service (crash) via a crafted message. | |||
=== CVE-2019-12587 === | |||
The EAP peer implementation in Espressif ESP-IDF 2.0.0 through 4.0.0 and ESP8266- | |||
NONOS-SDK 2.2.0 through 3.1.0 allows the installation of a zero Pairwise Master Key | |||
(PMK) after the completion of any EAP authentication method, which allows attack- | |||
ers in radio range to replay, decrypt, or spoof frames via a rogue access point. | |||
=== CVE-2020-12638 === | |||
An encryption-bypass issue was discovered on Espressif ESP-IDF devices through | |||
4.2, ESP8266-NONOS-SDK devices through 3.0.3, and ESP8266-RTOS-SDK devices | |||
through 3.3. Broadcasting forged beacon frames forces a device to change its authen- | |||
tication mode to OPEN, effectively disabling its 802.11 encryption. | |||
== Attack == | |||
=== CVE-2019-12587 === | |||
== Used Hardware == | == Used Hardware == | ||
Revision as of 11:32, 27 November 2020
Summary
The Pocket Science Lab Kit is a small USB-based hardware extension for an Android device or PC, which allows the use of different instruments / functions that are already integrated in the board or can be expanded via external sensors. It is aimed at everyone whether teacher, pupil, hobbyist, student, professor or scientist. The name Pocket Science Lab says it all. The user has a small scientific laboratory in the size of a pocket. The aim of the Pocket Science Lab project is to perceive one's environment better and to digitize the analog world.
Description
This board allows you to measure all kinds of things, assumed you have the right sensor, and it is supported. Basic connectors/sensors are USB, GPIO Connector, UART, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, I2C and ICSP Programmer. A full list of technical specifications can be found on the datasheet as well as on the PS Lab website. A built-in Oscilloscope, Power Source, Multimeter, Accelerometer, Sensors, Logic Analyzer and Wave Generator can be used right out of the box. A Temperature Sensor, Compass, Barometer and Lux Meter are not included and need to be bought separately.
Functionalities
To control the PS Lab Kit an Android App and PC application are available. From the user-friendly interface a list of various functions can be selected. The functions are listed in the section described above. Each function can record the received input. Therefore, a Rec-Button will appear in the top right corner. The recording can be started by clicking on it and stopped by clicking it another time on it. The menu has a section called: ”Logged Data”. In this section the recording can be found and exported as .CSV file.
Sensors
Notable sensors are the temperature sensor, gas sensor and moisture sensor.
Currently the functionalities of these sensors is unavailable for the PS Lab Kit. The Pocket Science Lab Project provides a list of compatible sensors.
Wi-Fi
ESP8266-DevKitC is a small-sized ESP8266-based development board produced by Espressif. All the I/O pins of the module are broken out into the female pin headers on both sides of the board for easy interfacing. Developers can connect these pins to peripherals as needed.
The Pocket Science Lab Kit can be extended with such a Wi-Fi module. Normally an ESP8266 chip would be soldered to the back of the kit to create network connectivity between the board and the Android phone or PC. The documentation for this is currently not available.
Use Cases
The following list consists of some basic use cases of the kit.
Multimeter
Multimeter text.
Oscilloscope
Oscilliscope text.
Exploits
CVE-2019-12586
The EAP peer implementation in Espressif ESP-IDF 2.0.0 through 4.0.0 and ESP8266- NONOS-SDK 2.2.0 through 3.1.0 processes EAP Success messages before any EAP method completion or failure, which allows attackers in radio range to cause a denial of service (crash) via a crafted message.
CVE-2019-12588
The client 802.11 mac implementation in Espressif ESP8266-NONOS-SDK 2.2.0 through 3.1.0 does not validate correctly the RSN AuthKey suite list count in beacon frames, probe responses, and association responses, which allows attackers in radio range to cause a denial of service (crash) via a crafted message.
CVE-2019-12587
The EAP peer implementation in Espressif ESP-IDF 2.0.0 through 4.0.0 and ESP8266- NONOS-SDK 2.2.0 through 3.1.0 allows the installation of a zero Pairwise Master Key (PMK) after the completion of any EAP authentication method, which allows attack- ers in radio range to replay, decrypt, or spoof frames via a rogue access point.
CVE-2020-12638
An encryption-bypass issue was discovered on Espressif ESP-IDF devices through 4.2, ESP8266-NONOS-SDK devices through 3.0.3, and ESP8266-RTOS-SDK devices through 3.3. Broadcasting forged beacon frames forces a device to change its authen- tication mode to OPEN, effectively disabling its 802.11 encryption.