Difference between revisions of "Princeton IoT Inspector"
Jostrowski (talk | contribs) (Add hardware link) |
Jostrowski (talk | contribs) m (typo) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Summary == | == Summary == | ||
Princeton IoT Inspector is an open-source desktop tool to automatically discovers IoT devices and analyzes their network traffic | Princeton IoT Inspector is an open-source desktop tool to automatically discovers IoT devices and analyzes their network traffic. | ||
== Requirements == | == Requirements == | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
The official installation guide can be found on the [https://iot-inspector.princeton.edu/blog/post/getting-started/ official web-page] | The official installation guide can be found on the [https://iot-inspector.princeton.edu/blog/post/getting-started/ official web-page] | ||
Here a tutorial how to install the IoT-Inspector on the Raspberry Pi: [[Princeton IoT Inspector: Installation on the Raspberry Pi]] | Here a tutorial on how to install the IoT-Inspector on the Raspberry Pi: [[Princeton IoT Inspector: Installation on the Raspberry Pi]] | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
=== View devices === | === View devices === | ||
Under | Under "My Devices" you will find all connected devices on your network | ||
You can now click on the device you want to monitor with the checkbox, | |||
Or if you want to monitor all devices you can select "monitor all devices" | |||
[[File:Iot inspector devices.png|border|800px]] | [[File:Iot inspector devices.png|border|800px]] | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
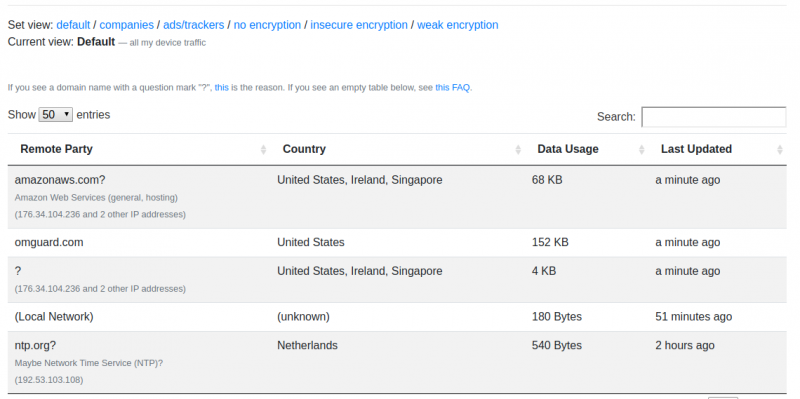
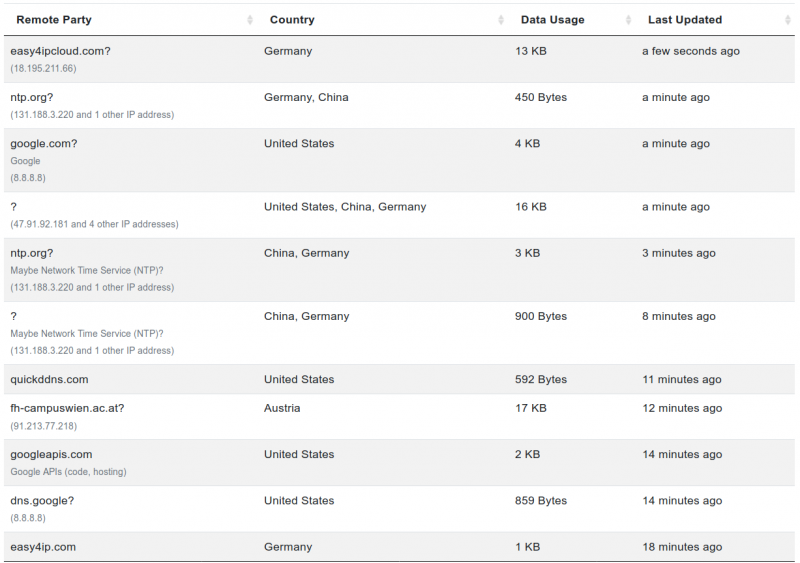
We can | We can analyze the connected IPs more closely when clicking on "communication endpoints" | ||
Latest revision as of 10:10, 30 January 2020
Summary
Princeton IoT Inspector is an open-source desktop tool to automatically discovers IoT devices and analyzes their network traffic.
Requirements
- Operating system: Linux (or Mac OS)
IoT Inspector
The official installation guide can be found on the official web-page
Here a tutorial on how to install the IoT-Inspector on the Raspberry Pi: Princeton IoT Inspector: Installation on the Raspberry Pi
Start IoT Inspector
Launch the IoT Inspector:
cd ~/princeton-iot-inspector/ ./linux-start-inspector.sh
You should be greeted with following screen:
===========================
Princeton IoT Inspector
===========================
View the IoT Inspector report at:
https://inspector.cs.princeton.edu/persistent/xxxx-xxxx-xxxx-xxxx
This is your private link. Open it only on trusted computers.
Hit Control + C to terminate this process and stop data collection.
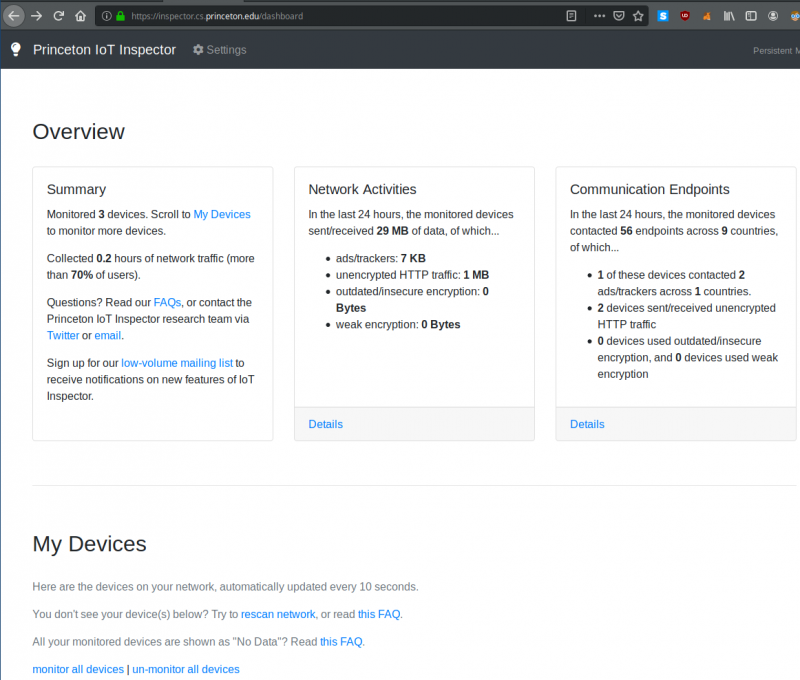
Overview
visit the website from the previous output from any device
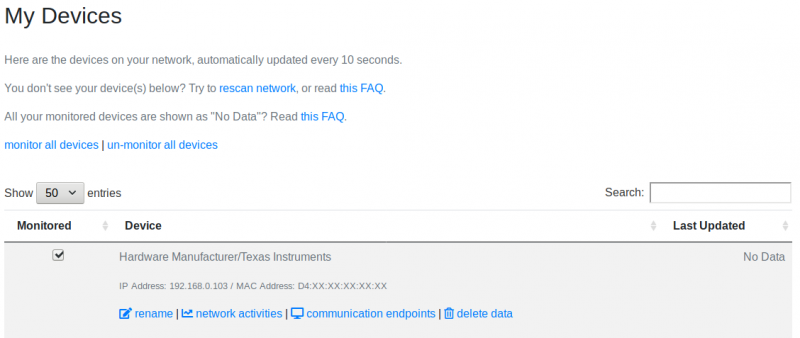
View devices
Under "My Devices" you will find all connected devices on your network
You can now click on the device you want to monitor with the checkbox,
Or if you want to monitor all devices you can select "monitor all devices"
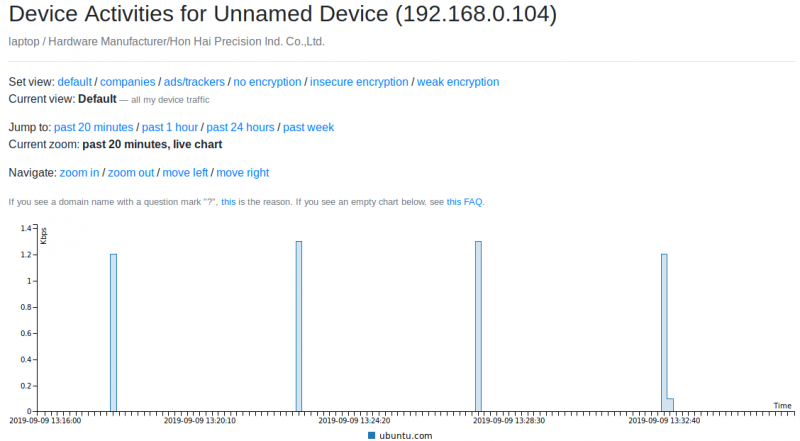
Network activities
Now it will get the network data
you can view it under "network activities"
Analyze ABUS PPIC32020 smart security WiFi camera
Connect the camera to the network, click "monitor device" in the iot-inspector dashboard.
Now it will arp spoof the connection and log the network traffic.
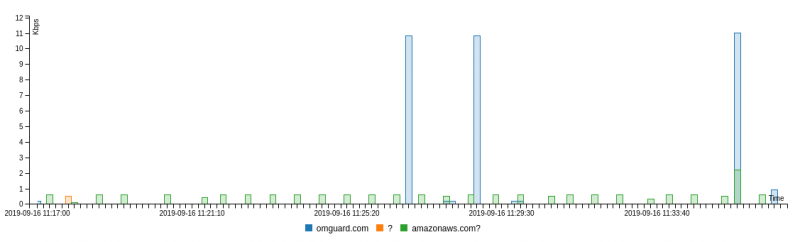
We can analyze the connected IPs more closely when clicking on "communication endpoints"
Analyze Technaxx WiFi smart alarm system starter kit TX-84
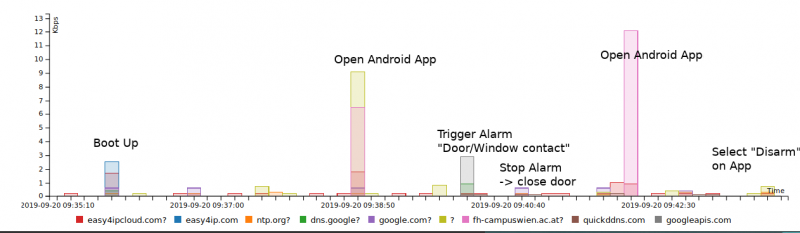
We can observe, that the alarm base station is very talkative.
Used Hardware
Raspberry Pi 3, Model B+, WLAN, BT
ABUS PPIC32020 smart security WiFi camera
Technaxx WiFi smart alarm system starter kit TX-84