Web Application Analysis
Summary
Web Application Analysis is engaged in finding and vulnerabilities and if necessary to harden current security measures. The analysing process should be contemplated for every web application. It might reveal exploits that would cause devastating consequences. Unprotected websites and web applications are targeted by hackers and often lead to database leaks, theft of banking information and infringement of privacy. Many companies are not technically adept and therefore cannot evaluate the possible damage, hoping to save costs in the development phase by skipping the web application analysis. [1] [2]
Web Application Security
Web application analysis is a branch in the IT security field that deals with web vulnerabilities and how to find them.
Security Threats
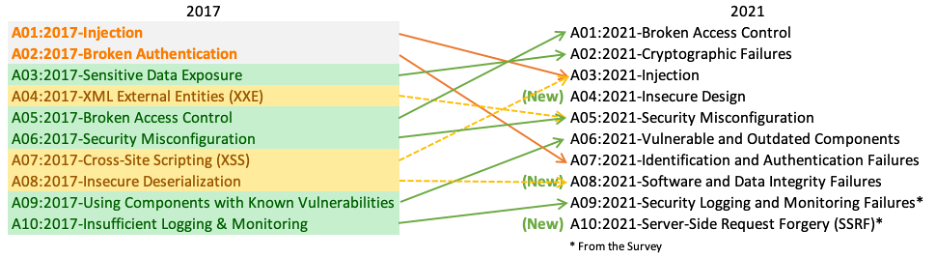
There is a magnitude of security threats that can occur in a website or web application. The Open Web Application Security Projekt (OWASP) publishes every four years the OWASP Top 10 report, including the ten most occurring security threats. Here is a comparison between the year 2017 and the year 2021:
These vulnerabilities are easily avoidable but end up over and over on the Top 10 list. One common reason for them being this high listed is the lack of knowledge of the developer. Because knowledge and understanding of the possible threats are so important, there are many test and learning platforms specially made to train and improve best practice security policies.
Web Application Scanning Tool
It is possible to perform web application analysis by hand but it is slower and mistakes can more easily happen. Using software tools created for finding vulnerabilities the efficiency increases significantly. For this purpose were a bunch of tools developed. A few of those are:
- skipfish
- ZAP
- WpScan
- sqlmap
- commix
- ...
Many tools come pre-installed with Kali Linux. They are used for information gathering, exploitation and testing throughout the development of web applications. These tools run a set of tests to see how the application reacts and analyses those reactions. Depending on the kind of reaction the tools recieve they evaluate if an attack could be accomplished or not. The positive/false ratio is usually pretty low, which is an indication of how accurate they are.
There are 3 ways to test web applications: static, dynamic or interactive.
Static Application Security Testing (SAST)
Static Application Security Testing is also called white-box testing. It is a testing method where the source code is available to the tester. Using code reviews and analysing tools mistakes can be corrected. This technique is usually only used internally because access to the code needs to be granted.
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST)
Dynamic Application Security Testing is the testing method that first comes to mind when talking about web application analysis. It can be done by anyone because it does not require access to the source code of the application. This technique is a black-box testing method, meaning the structure is hidden and information can only be assumed by sending requests and analysing the responses. The tools mentioned in this article are all DAST tools.
Interactive Application Security Testing (IAST)
Contrary to SAST and DAST, IAST analyses threats in real-time while the application is executed and work from inside of the web application. Usually, it gets combined with the other testing methods to simulate an attacker trying to break in.
Commix
Commix, which stands for [Comm]and [I]njection E[x]ploiter, is an open-source penetration testing tool. It is used to find and exploit command injection vulnerabilities in web applications. Cite error: Closing </ref> missing for <ref> tag
[1]
[4]
[5]
[6]
[7]
[8]
</references>
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 https://blog.stackpath.com/web-application/
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs nameddef1 - ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedtop10 - ↑ https://www.w4rri0r.com/hacking-tools-windows-os-x-linux-android-solaris-unixware/web-application-analysis.html
- ↑ https://www.imperva.com/learn/application-security/application-security-testing/
- ↑ https://www.kali.org/tools/commix/
- ↑ https://code.google.com/archive/p/skipfish/
- ↑ https://owasp.org/