USB Armory
Introduction
Launched in 2014, USB Armory is a small and portable USB-sized personal computer created by Andrea Barisani [1]. Originally intended to be produced as a secure data store, USB Armory managed to become a versatile device with the development of its Hardware and Software. With its hardware sufficient as a computer, it can be configured on an installed Linux system that boots and thus powers up when plugged into any computer, for example, so that data not only ends up on an encrypted partition but is automatically re-encrypted when transferred [2] .
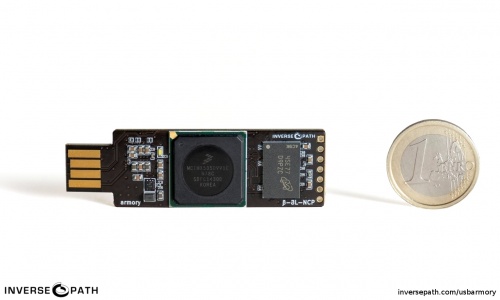
Hardware
- NXP i.MX53 ARM® Cortex™-A8 800MHz, 512MB DDR3 RAM
- USB host powered (<500 mA) device with compact form factor (65 x 19 x 6 mm)
- ARM® TrustZone®, secure boot + storage + RAM
- microSD card slot
- 5-pin breakout header with GPIOs and UART
- customizable LED, including secure mode detection
- excellent native support (Android, Debian, Ubuntu, Arch Linux)
- USB device emulation (CDC Ethernet, mass storage, HID, etc.)
- Open Hardware & Software [4]
Software
- Native Linux support – creating boot images is easy
- Precompiled images are available for Debian 9 (Stretch) and Arch Linux, with more on the way
- USB device emulation (CDC Ethernet, mass storage, HID, etc.) [5]
How to connected
- HS USB 2.0 On-The-Go (OTG) with device emulation
- TCP/IP communication via CDC Ethernet emulation
- flash drive functionality via mass storage device emulation
- serial communication over USB or physical UART
- stand-alone mode with dedicated host adapter [6]
Application examples
- Hardware Security Module (HSM)
- file storage with advanced features such as automatic encryption, virus scanning, host authentication and data self-destruct
- OpenSSH client and agent for untrusted hosts (kiosk)
- router for end-to-end VPN tunnelling, Tor
- password manager with integrated web server
- electronic wallet (e.g. pocket Bitcoin wallet)
- authentication token
- portable penetration testing platform
- low level USB security testing [7]
Getting Started
Boot Mechanisms
In order for USB Armory to work in a certain operating system, either the microSD card inserted. [8]:
USB Armory has a valid Pre-Image file for each operating system on its own page. Optionally, booting can be done either manually or by downloading the appropriate file and flashing the microSD card (before it is inserted into the USB Armory) with balenaEtcher software [9].
1. Step
You can find the following Pre-Image files at this link: https://github.com/f-secure-foundry/usbarmory/wiki/Available-images
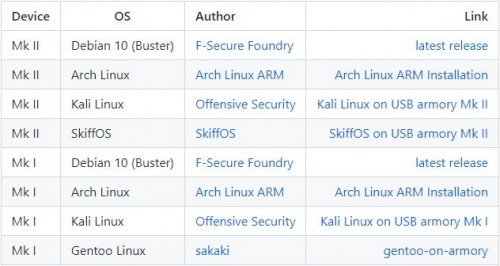
2. Step
You can download the following software here: https://www.balena.io/etcher/
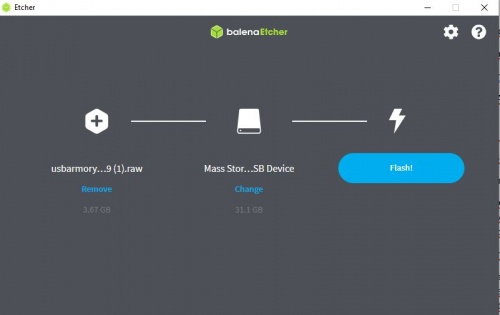
Host communication
Since the booted microSD card is ready in the operating system, Host communication can be started [12].
# look up the name of the USB virtual Ethernet interface which was created by the USB Armory ifconfig
# bring the USB virtual Ethernet interface up /sbin/ip link set usb0 up
# set the host IP address /sbin/ip addr add 10.0.0.2/24 dev usb0
# enable masquerading for outgoing connections towards wireless interface /sbin/iptables -t nat -A POSTROUTING -s 10.0.0.1/32 -o wlan0 -j MASQUERADE
# enable IP forwarding sudo sysctl -w net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
#connect to USB Armory via ssh - password: USB armory ssh usbarmory@10.0.0.1
#install Lynx Web browser on USB Armory sudo apt-get install Lynx
#launch Lynx Web browser on USB Armory lynx google.com
Hardware Used
References
- ↑ Andrea Barisani. Forging the USB armory, https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=bE5licRHMFs ,2014.
- ↑ NXP Community, Introducing USB armory, an Open Source Hardware Freescale i.MX53 Dongle , https://community.nxp.com/t5/i-MX-Solutions-Knowledge-Base/Introducing-USB-armory-an-Open-Source-Hardware-Freescale-i-MX53/ta-p/1126823, 2014
- ↑ Inverse Path, OPEN SOURCE FLASH-DRIVE SIZED COMPUTER, https://inversepath.com/usbarmory_mark-one.html
- ↑ Inverse Path, Hardware, https://inversepath.com/usbarmory_mark-one.html
- ↑ Andrea Barisani, MK II Introduction, https://github.com/f-secure-foundry/usbarmory/wiki/Mk-II-Introduction#software
- ↑ Inverse Path, How to Connect, https://inversepath.com/usbarmory_mark-one.html
- ↑ Inverse Path, Applications, https://inversepath.com/usbarmory_mark-one.html
- ↑ Getting started, https://github.com/f-secure-foundry/usbarmory/wiki/Starting#getting-started
- ↑ Cite error: Invalid
<ref>tag; no text was provided for refs namedAnd - ↑ Andrea Barisani, Available images, https://github.com/f-secure-foundry/usbarmory/wiki/Available-images
- ↑ balenaEtcher, https://www.balena.io/etcher/
- ↑ Andrea Barisani, Setup & Connection Sharing: Linux , https://github.com/f-secure-foundry/usbarmory/wiki/Host-communication#setup--connection-sharing-linux